VV / VN ECMO
- Home


Who we are
Understanding the Different ECMO Support Systems
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) is an advanced life-support therapy used when the heart and/or lungs are unable to function adequately despite maximal medical treatment. Depending on the patient’s condition, different types of ECMO are used to provide targeted support.
There are three main types of ECMO, each designed for specific cardiac and respiratory conditions.
Veno-Venous (VV) ECMO
Advanced Support for Severe Lung Failure
VV ECMO is primarily used for patients with severe respiratory failure when the lungs are unable to provide adequate oxygen or remove carbon dioxide, but the heart function remains relatively stable.
Blood is drained from a large vein, passed through an artificial lung (oxygenator) where oxygen is added and carbon dioxide is removed, and then returned to the venous system. This process allows the lungs to rest and recover while oxygenation is maintained.
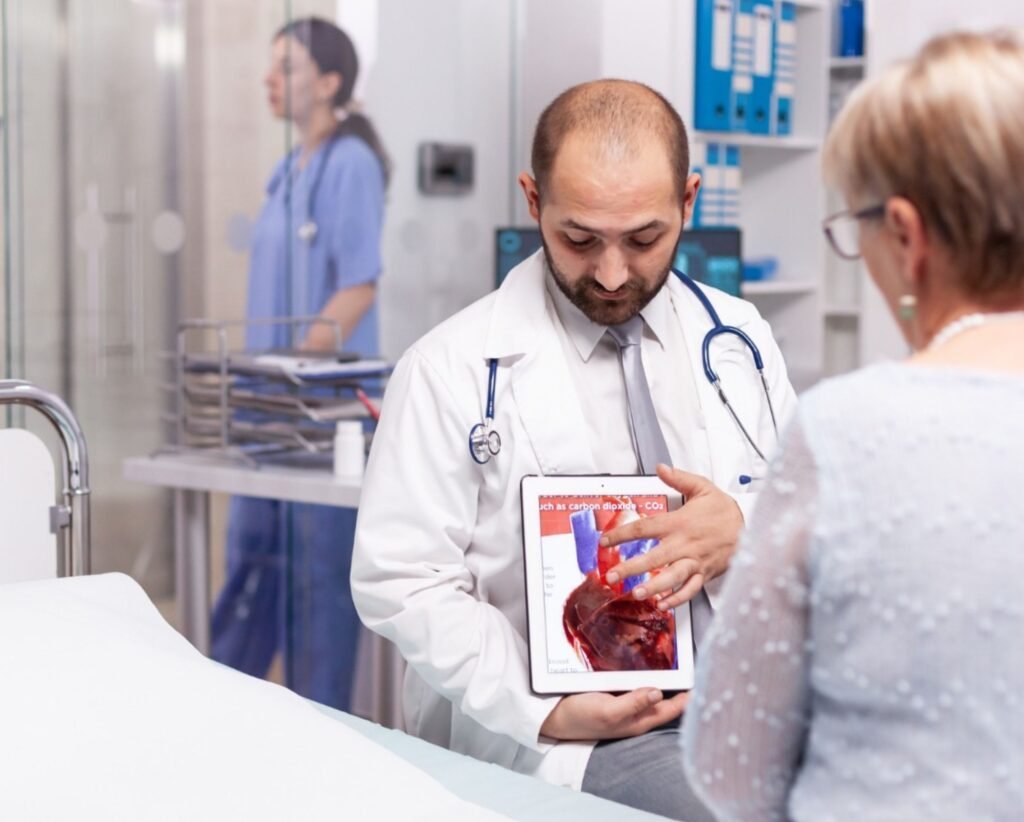
Our Services
Conditions Treated
with VV ECMO
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Severe pneumonia
- Viral lung infections
- Aspiration-related lung injury
- Respiratory failure unresponsive to ventilator support
Benefits
Key Benefits of VV ECMO
01
Supports lung function without stressing the heart
02
Improves oxygen levels and carbon dioxide removal
03
Allows lung healing while reducing ventilator-related injury
Veno-Arterial (VA) ECMO
Life-Saving Support for Heart and Lung Failure
VA ECMO is used when both heart and lung function are severely compromised. It provides full cardiopulmonary support by assisting blood circulation and oxygenation simultaneously.
Blood is drained from a large vein and returned to an artery after oxygenation, allowing ECMO to replace the pumping function of the heart and the oxygenation function of the lungs.

Our Services
Conditions Treated
with VA ECMO
- Cardiogenic shock
- Acute heart failure
- Cardiac arrest
- Post-cardiac surgery complications
- Severe myocardial infarction
Benefits
Key Benefits of VA ECMO
01

Provides immediate circulatory and oxygen support
02

Stabilizes patients in life-threatening cardiac conditions
03

Acts as a bridge to recovery, surgery, or transplantation

